Traditional mechanisms for cross-border payments in international trade rely on banking networks, financial institutions, and specialized payment systems. However, they are characterized by inefficiency and limited accessibility for developing countries. The average transfer time is 3 to 5 days, while high fees create unequal conditions for businesses. These factors, along with sanctions, drive the search for new solutions.
According to the Central Bank of Russia, one in four Russian exporting companies faces payment delays or blockages. Challenges are particularly severe with Chinese partners due to the risk of secondary U.S. sanctions. To bypass restrictions, companies use intermediaries, increasing transaction costs to 6%. Barter transactions, enabling exchanges without money, are another common practice. However, these methods come with market risks and high costs.

A promising direction is digital payments based on distributed ledger technology. These offer advantages such as high transaction speed, lower costs by eliminating intermediaries, improved financial inclusion, and resistance to sanctions. However, legal frameworks and infrastructure investments are needed for implementation.
Cryptocurrencies are becoming a relevant tool for circumventing restrictions. In the EAEU countries, efforts are underway to regulate cryptocurrencies, including mining, taxation, and preventing illicit use. Cryptocurrencies provide a decentralized approach but are associated with risks and are considered a temporary solution.
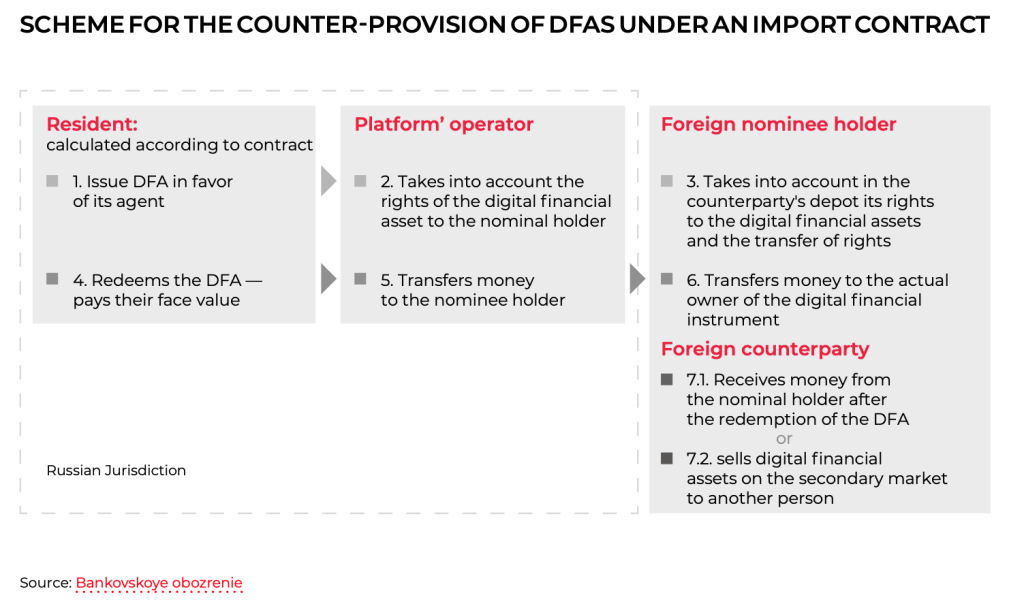
Another innovative tool is digital financial assets (DFAs), backed by various assets. In Russia, DFAs are legally regulated, allowing their use in foreign trade settlements under specific conditions, such as requiring contracts to stipulate the exchange of DFAs. Additionally, foreign digital rights (FDRs) can be used on Russian platforms, expanding export opportunities.
Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) are seen as the most promising solution. They can integrate national systems and enhance resilience to external challenges. CBDCs are particularly appealing for intergovernmental blocs like the EAEU and BRICS, where nations aim to reduce dependence on global financial players.
Overall, digital technologies are transforming international trade, making payments faster, cheaper, and more transparent. However, challenges related to regulation and security remain, necessitating continued development of the necessary infrastructure.



